一、正常出现异常
Controller:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| @RestController
public class ErrorController {
@GetMapping("/diyError")
public String error() {
int i = 2 / 0;
return "diyError";
}
}
|
结果:

可以看见此错误页是 SpringBoot 提供的,由于我们没有提供 /error 页面,顺便展示我们出现的错误
二、静态页面异常
在 static 目录下新建一个 error 目录,并在其中新建 404.html 和 500.html:
404.html:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>404</h1>
</body>
</html>
|
500.html:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>500</h1>
</body>
</html>
|
再次访问 http://localhost:8080/diyError
可以看见已经进入自定义的静态页面了:
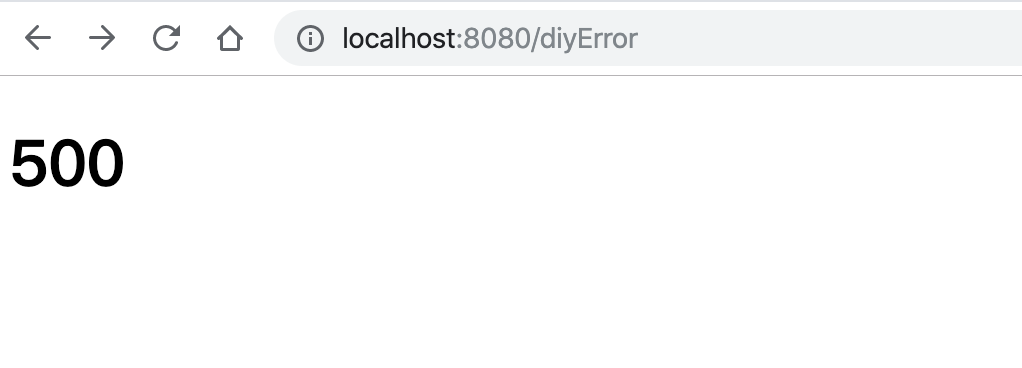
再访问一个不存在的页面:
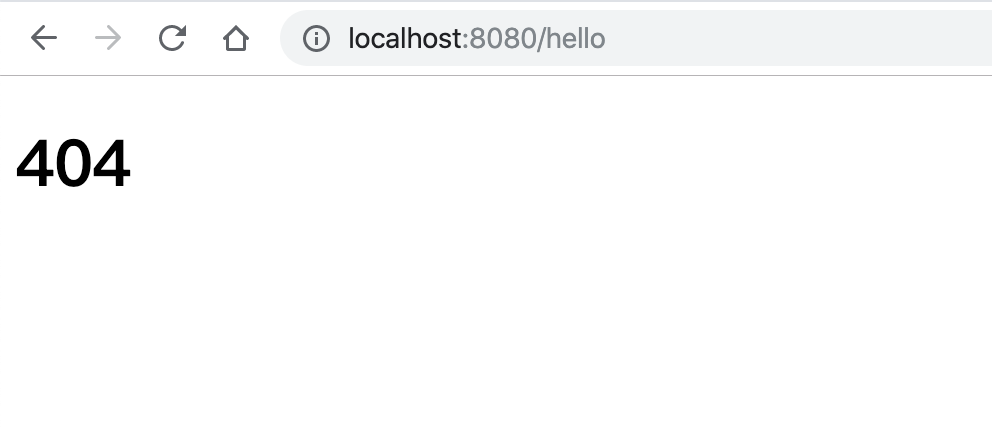
注:也可以只定义 4xx.html 与 5xx.html 的静态页面,只要发生 400-499 的状态码或者 500-599 的状态码就对应 4xx.html 与 5xx.html 的结果
三、动态页面异常
引入 thymeleaf 的依赖:
1
2
3
4
| <dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
|
在 templates 目录下新建一个 error 目录,并在其中新建 404.html、 500.html、 4xx.html、5xx.html :

再次访问 http://localhost:8080/diyError
可以看见已经进入自定义的动态页面了:
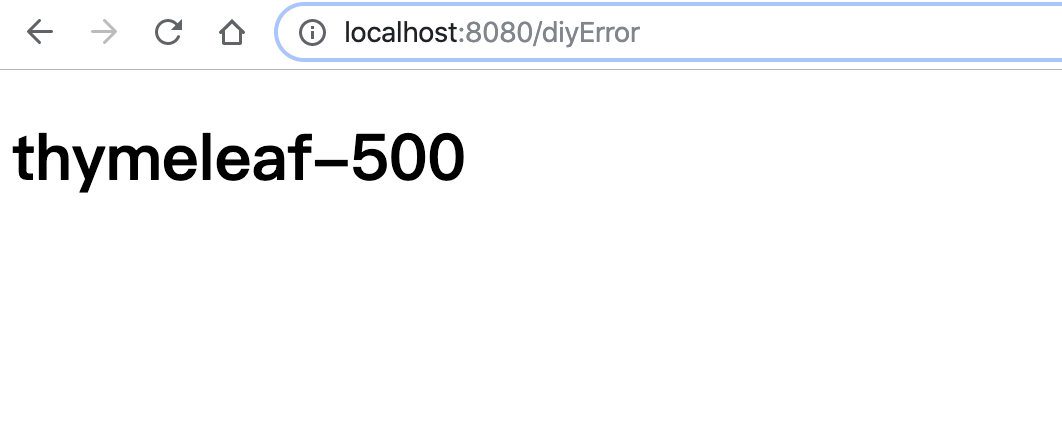

优先级:
- 如果有 404 的页面,会先找 404.html;如果没有就会找 4xx.html
- 如果动态页面和静态页面同时存在,会优先使用动态页面
完整顺序大概如下:
发生了500错误 –> 查找动态 500.html 页面 –> 查找静态 500.html –> 查找动态 5xx.html –> 查找静态 5xx.html
四、SpringBoot 怎么自动配置
关键类:ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| @Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
static class DefaultErrorViewResolverConfiguration {
private final ApplicationContext applicationContext;
private final ResourceProperties resourceProperties;
DefaultErrorViewResolverConfiguration(ApplicationContext applicationContext,
ResourceProperties resourceProperties) {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
this.resourceProperties = resourceProperties;
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnBean(DispatcherServlet.class)
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(ErrorViewResolver.class)
DefaultErrorViewResolver conventionErrorViewResolver() {
return new DefaultErrorViewResolver(this.applicationContext, this.resourceProperties);
}
}
|
在默认的错误视图解析器 DefaultErrorViewResolver 中:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| @Override
public ModelAndView resolveErrorView(HttpServletRequest request, HttpStatus status, Map<String, Object> model) {
ModelAndView modelAndView = resolve(String.valueOf(status.value()), model);
if (modelAndView == null && SERIES_VIEWS.containsKey(status.series())) {
modelAndView = resolve(SERIES_VIEWS.get(status.series()), model);
}
return modelAndView;
}
|
如果 modelAndView 为空,即没找到对应的具体 404.html,就会用 SERIES_VIEWS.containsKey(status.series()) 找 4xx.html
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| private ModelAndView resolve(String viewName, Map<String, Object> model) {
String errorViewName = "error/" + viewName;
TemplateAvailabilityProvider provider = this.templateAvailabilityProviders.getProvider(errorViewName,
this.applicationContext);
if (provider != null) {
return new ModelAndView(errorViewName, model);
}
return resolveResource(errorViewName, model);
}
|
- 判断 error 文件夹下面是否有对应的状态码的文档
- 再判断是否有动态页面,即 TemplateAvailabilityProvider
- 如果是动态页面,就返回动态页面;否则返回静态页面
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| private ModelAndView resolveResource(String viewName, Map<String, Object> model) {
for (String location : this.resourceProperties.getStaticLocations()) {
try {
Resource resource = this.applicationContext.getResource(location);
resource = resource.createRelative(viewName + ".html");
if (resource.exists()) {
return new ModelAndView(new HtmlResourceView(resource), model);
}
}
catch (Exception ex) {
}
}
return null;
}
|
五、自定义异常数据
在 ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration 中,处理异常数据的方法:
1
2
3
4
5
| @Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = ErrorAttributes.class, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT)
public DefaultErrorAttributes errorAttributes() {
return new DefaultErrorAttributes();
}
|
在 DefaultErrorAttributes() 中通过设置参数得到相应的结果
例如:将 error 中的 5xx.html 改为:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>5xx</h1>
<table border="1">
<tr>
<td>path</td>
<td th:text="${path}"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>error</td>
<td th:text="${error}"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>message</td>
<td th:text="${message}"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>timestamp</td>
<td th:text="${timestamp}"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>status</td>
<td th:text="${status}"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>trace</td>
<td th:text="${trace}"></td>
</tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>
|
此时仔运行结果:
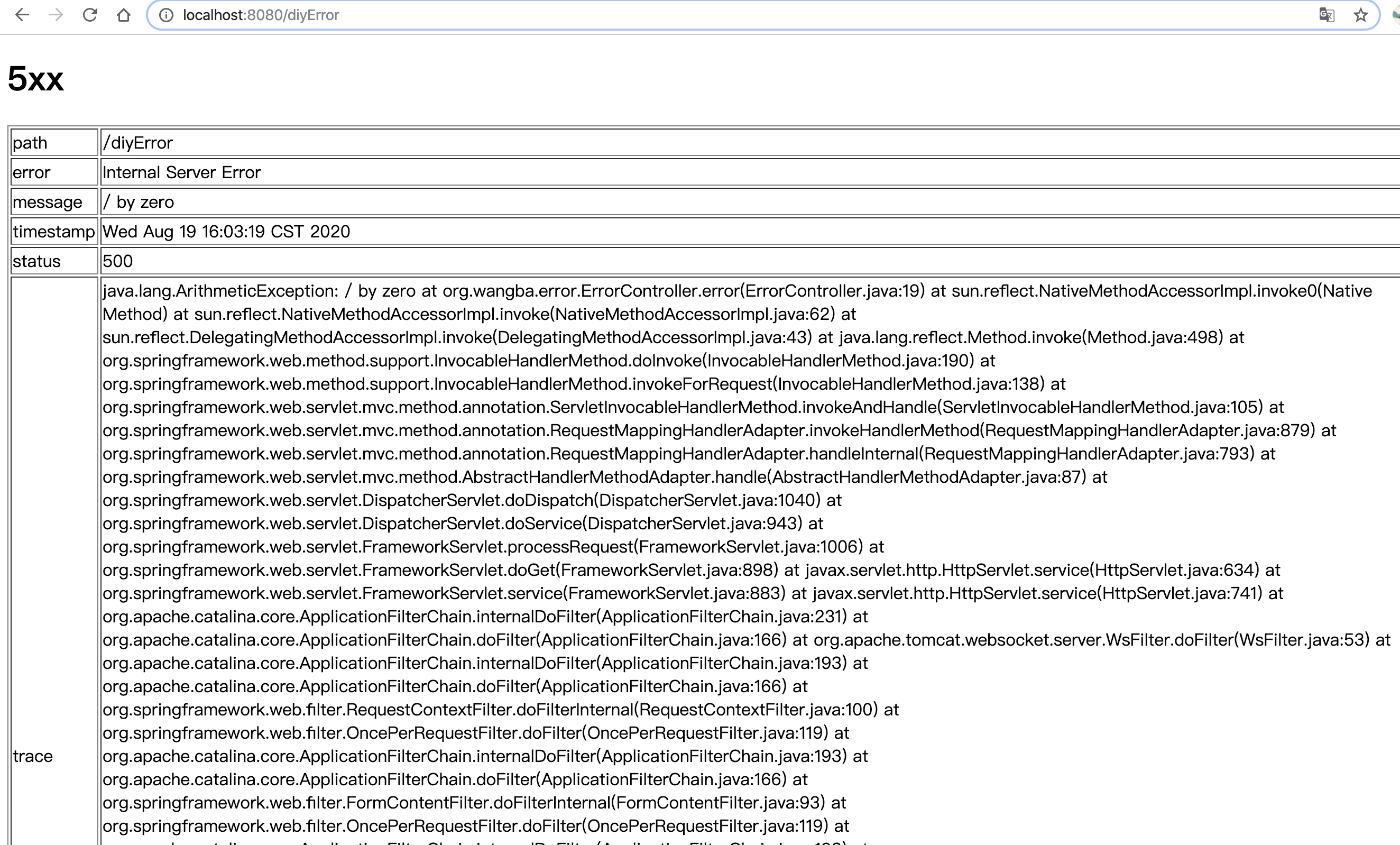
再看一下使 DefaultErrorAttributes 生效的条件:
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = ErrorAttributes.class, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT)
所以只要我们自定义 ErrorAttributes.class 就可以实现自己定义的异常数据处理
自定义 ErrorAttributes 有两种方式 :
- 直接实现 ErrorAttributes 接口
- 继承 DefaultErrorAttributes(推荐),因为 DefaultErrorAttributes 中对异常数据的处理已经完成,开发者可以直接使用。
新建一个配置类继承 DefaultErrorAttributes
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| @Component
public class MyErrorConfig extends DefaultErrorAttributes {
@Override
public Map<String, Object> getErrorAttributes(WebRequest webRequest, ErrorAttributeOptions options) {
Map<String, Object> errorAttributes = super.getErrorAttributes(webRequest, options);
errorAttributes.put("myerror", "自定义异常");
return errorAttributes;
}
}
|
在 5xx.html 中加入:
1
2
3
4
| <tr>
<td>myerror</td>
<td th:text="${myerror}"></td>
</tr>
|
运行结果:可以看到此时的自定义的 error 已经加入






