一、OverView
在上一篇文章中介绍了一下 Spring Data JPA 的一下简单的 CRUD,但是在公司业务中,不可能这么简单;且在业务中大部分都是查询业务,具体点就是动态查询,什么单表多条件查询、多表多条件查询等等……
注:使用环境还是和上一篇一样
二、自定义SQL查询
如果想和这里面写原生的 SQL 语句,只要在 repository 中这样写就行:
1 |
|
注:
- 如果要写原生 SQL,@Query 注解中的 nativeQuery 要设置为 true,默认为 false
- 函数名设置的不能与自带的冲突,例如:findById,如果设置了一样,就会导致使用的自带的 API 进行查询,而不是自定义的,如果真的想使用自定义覆盖自带的,可以在实体类上使用 @NamedQueries 注解
在这里我们就使用 @Test 进行测试:
还有一种使用 JPQL 语法的查询方式:
repository:
1 |
|
Test:
关于 JPQL:和在 SQL 中一样,JPQL 中的 select 语句用于执行查询。其语法可表示为:select_clause form_clause [where_clause] [groupby_clause] [having_clause] [orderby_clause]
其中:
- from 子句是查询语句的必选子句。
- select 用来指定查询返回的结果实体或实体的某些属性。
- from 子句声明查询源实体类,并指定标识符变量(相当于SQL表的别名)。
- 如果不希望返回重复实体,可使用关键字 distinct 修饰。select、from 都是 JPQL 的关键字,通常全大写或全小写,建议不要大小写混用。
在 JPQL 中,查询所有实体的 JPQL 查询语句很简单,如下:select o from Order o 或 select o from Order as o
这里关键字 as 可以省去,标识符变量的命名规范与 Java 标识符相同,且区分大小写
更多参考:官网文档
三、自定义简单查询
在 Spring Data JPA 的官网也介绍了这种方式,一般这种方式在一些小项目中也经常使用:
| Keyword | Sample | JPQL snippet |
|---|---|---|
And |
findByLastnameAndFirstname |
… where x.lastname = ?1 and x.firstname = ?2 |
Or |
findByLastnameOrFirstname |
… where x.lastname = ?1 or x.firstname = ?2 |
Is, Equals |
findByFirstname,findByFirstnameIs,findByFirstnameEquals |
… where x.firstname = ?1 |
Between |
findByStartDateBetween |
… where x.startDate between ?1 and ?2 |
LessThan |
findByAgeLessThan |
… where x.age < ?1 |
LessThanEqual |
findByAgeLessThanEqual |
… where x.age <= ?1 |
GreaterThan |
findByAgeGreaterThan |
… where x.age > ?1 |
GreaterThanEqual |
findByAgeGreaterThanEqual |
… where x.age >= ?1 |
After |
findByStartDateAfter |
… where x.startDate > ?1 |
Before |
findByStartDateBefore |
… where x.startDate < ?1 |
IsNull, Null |
findByAge(Is)Null |
… where x.age is null |
IsNotNull, NotNull |
findByAge(Is)NotNull |
… where x.age not null |
Like |
findByFirstnameLike |
… where x.firstname like ?1 |
NotLike |
findByFirstnameNotLike |
… where x.firstname not like ?1 |
StartingWith |
findByFirstnameStartingWith |
… where x.firstname like ?1 (parameter bound with appended %) |
EndingWith |
findByFirstnameEndingWith |
… where x.firstname like ?1 (parameter bound with prepended %) |
Containing |
findByFirstnameContaining |
… where x.firstname like ?1 (parameter bound wrapped in %) |
OrderBy |
findByAgeOrderByLastnameDesc |
… where x.age = ?1 order by x.lastname desc |
Not |
findByLastnameNot |
… where x.lastname <> ?1 |
In |
findByAgeIn(Collection<Age> ages) |
… where x.age in ?1 |
NotIn |
findByAgeNotIn(Collection<Age> ages) |
… where x.age not in ?1 |
True |
findByActiveTrue() |
… where x.active = true |
False |
findByActiveFalse() |
… where x.active = false |
IgnoreCase |
findByFirstnameIgnoreCase |
… where UPPER(x.firstame) = UPPER(?1) |
原理大概如下:
假如创建如下的查询:findByUserDepUuid(),框架在解析该方法时,首先剔除 findBy,然后对剩下的属性进行解析
- 先判断 userDepUuid (根据 POJO 规范,首字母变为小写)是否为查询实体的一个属性,如果是,则表示根据该属性进行查询;如果没有该属性,继续第二步;
- 从右往左截取第一个大写字母开头的字符串此处为Uuid),然后检查剩下的字符串是否为查询实体的一个属性,如果是,则表示根据该属性进行查询;如果没有该属性,则重复第二步,继续从右往左截取;最后假设user为查询实体的一个属性;
- 接着处理剩下部分(DepUuid),先判断 user 所对应的类型是否有depUuid属性,如果有,则表示该方法最终是根据
Doc.user.depUuid的取值进行查询;否则继续按照步骤 2 的规则从右往左截取,最终表示根据Doc.user.dep.uuid的值进行查询。 - 可能会存在一种特殊情况,比如 Doc包含一个 user 的属性,也有一个 userDep 属性,此时会存在混淆。可以明确在属性之间加上 “_” 以显式表达意图,比如
findByUser_DepUuid()或者findByUserDep_uuid()
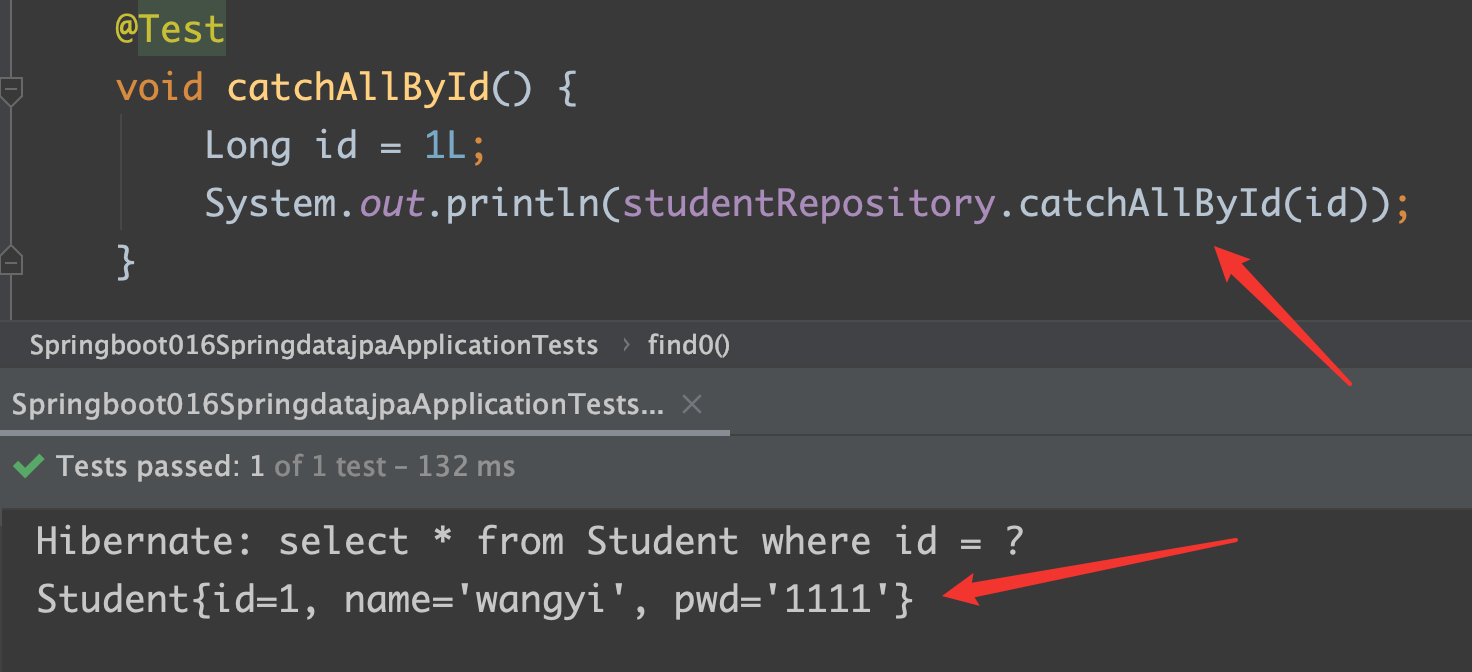
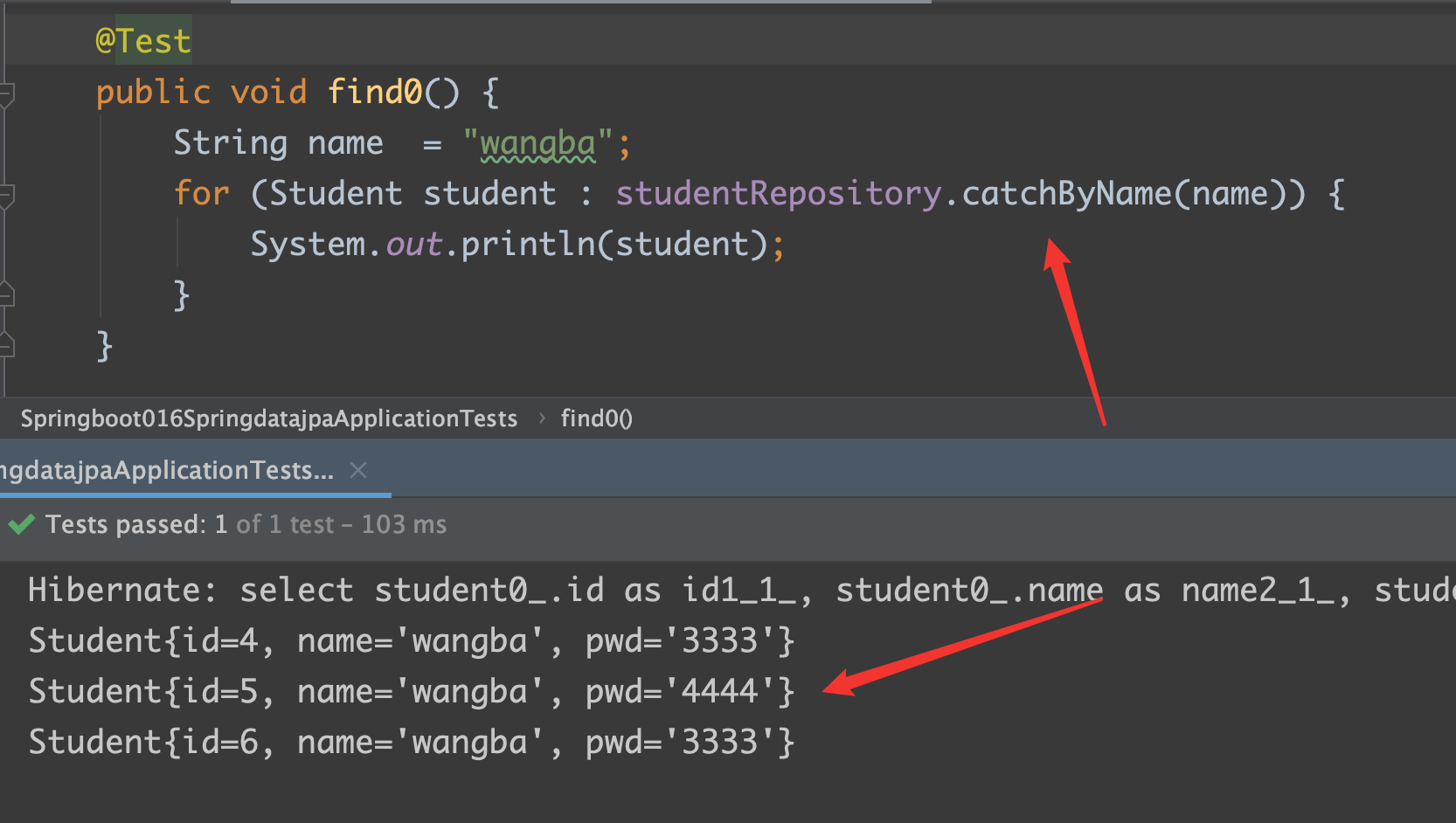
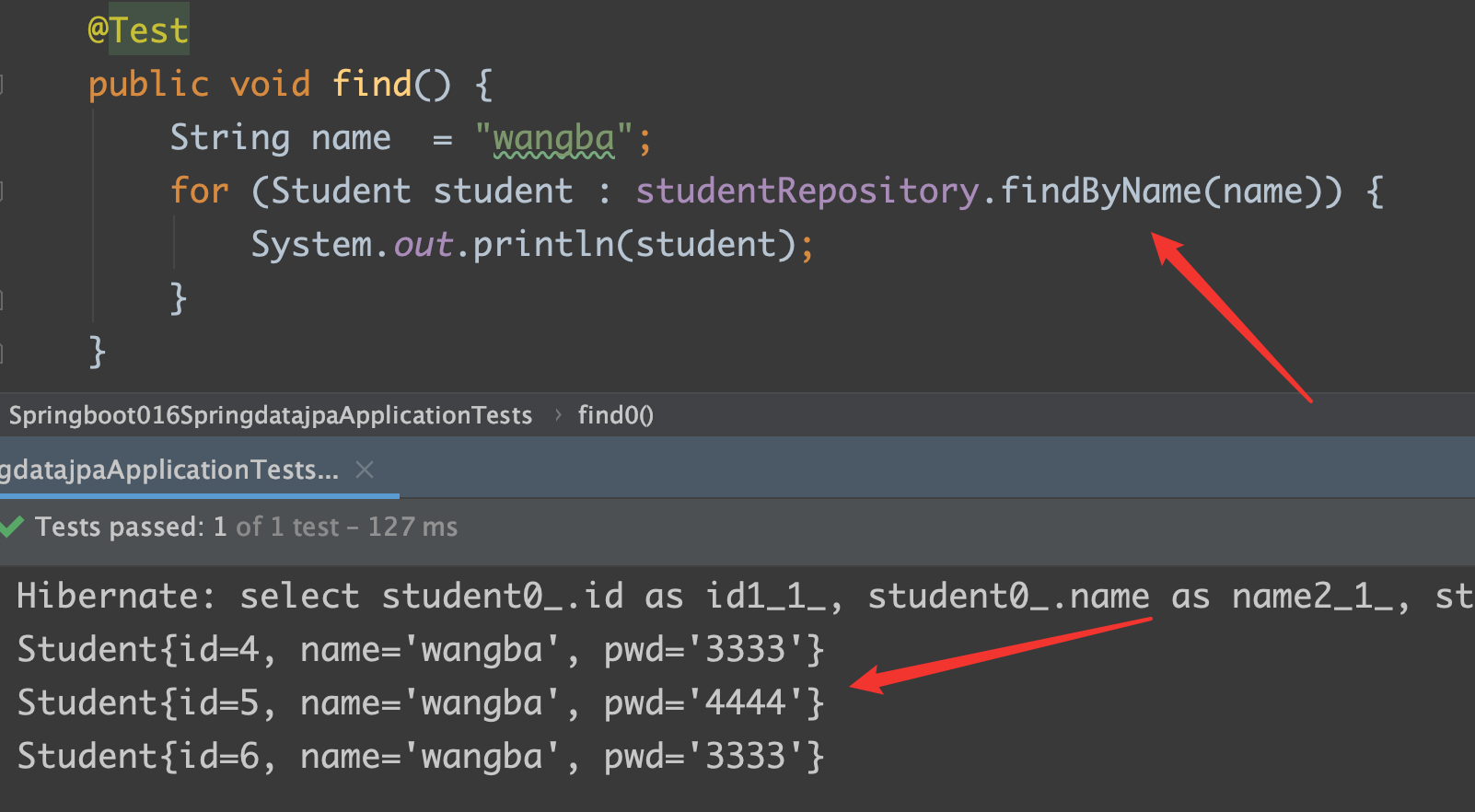
repository:
1 | List<Student> findByName(String name); |
test:
findByName
findByNameAndPwd
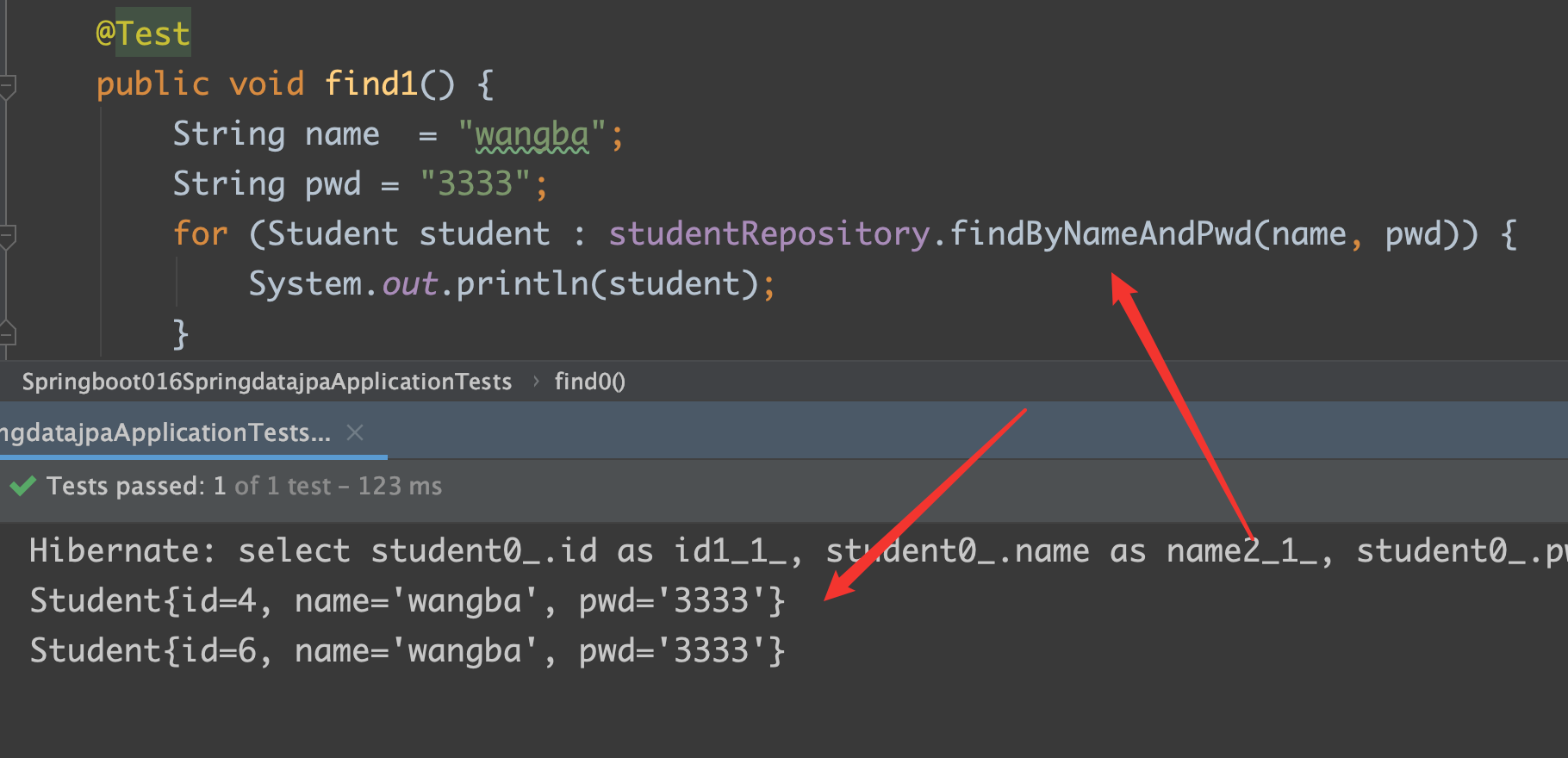
findByNameStartingWith
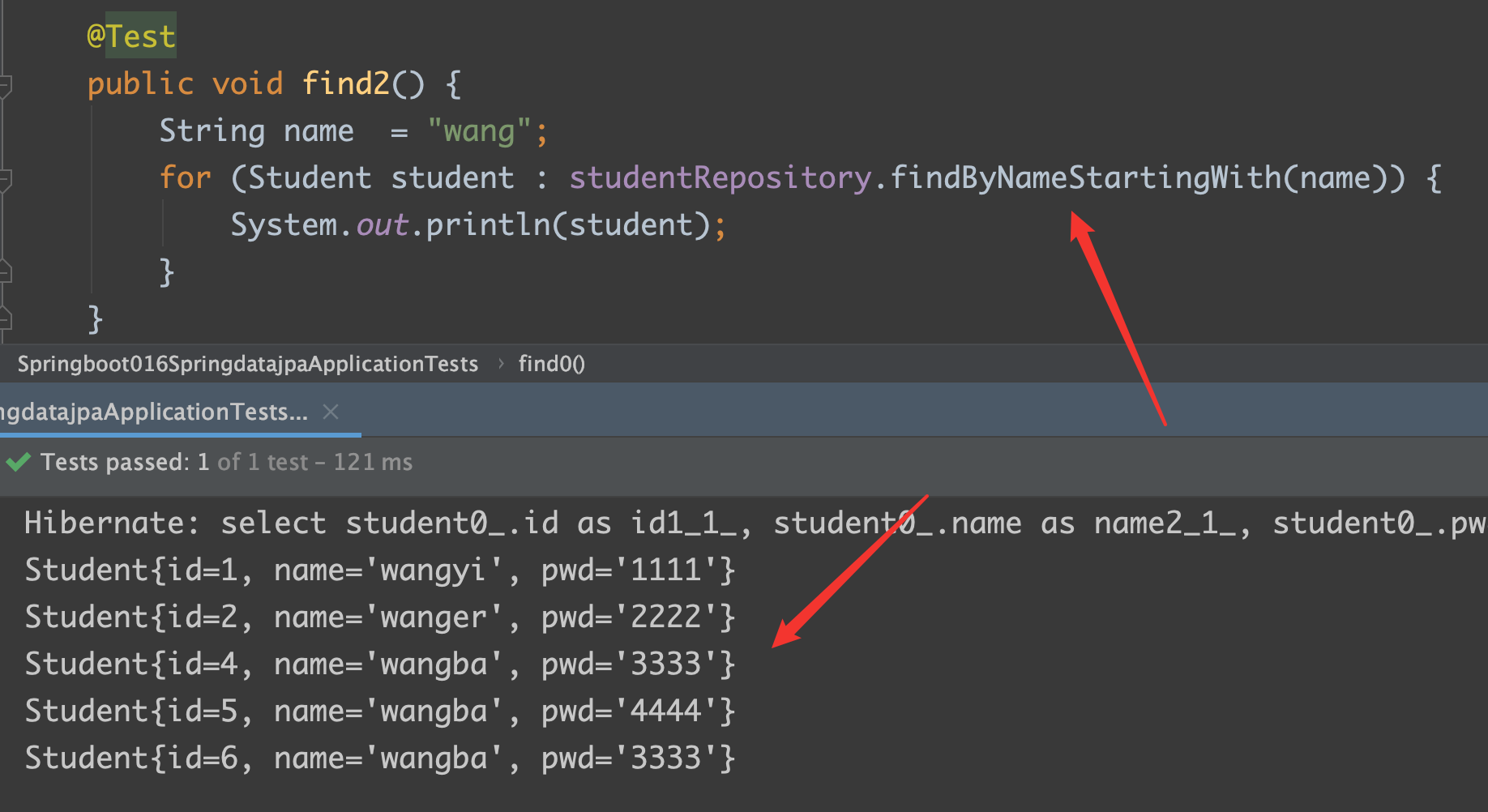
findByNameEndingWith
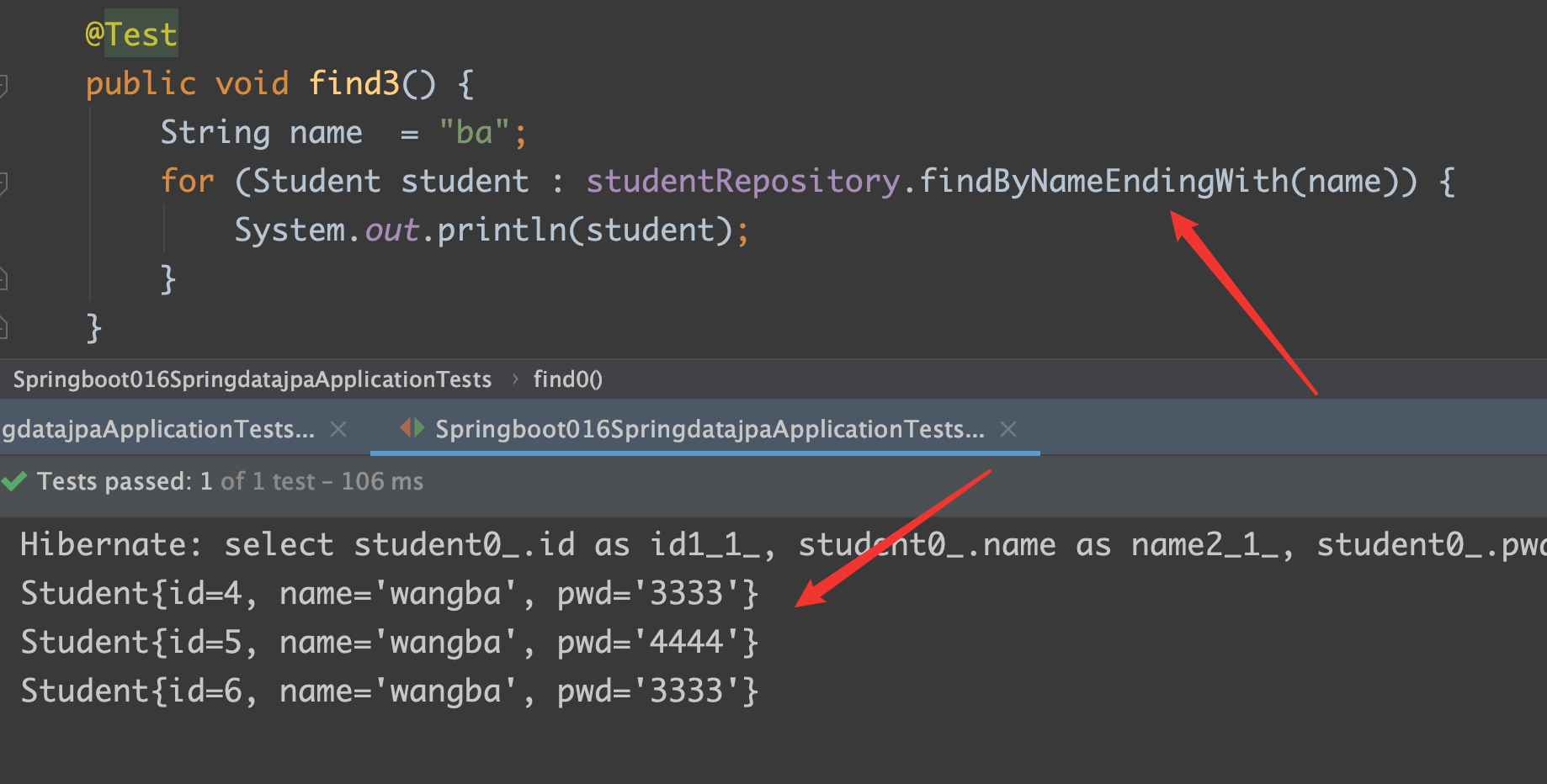
findByNameContaining
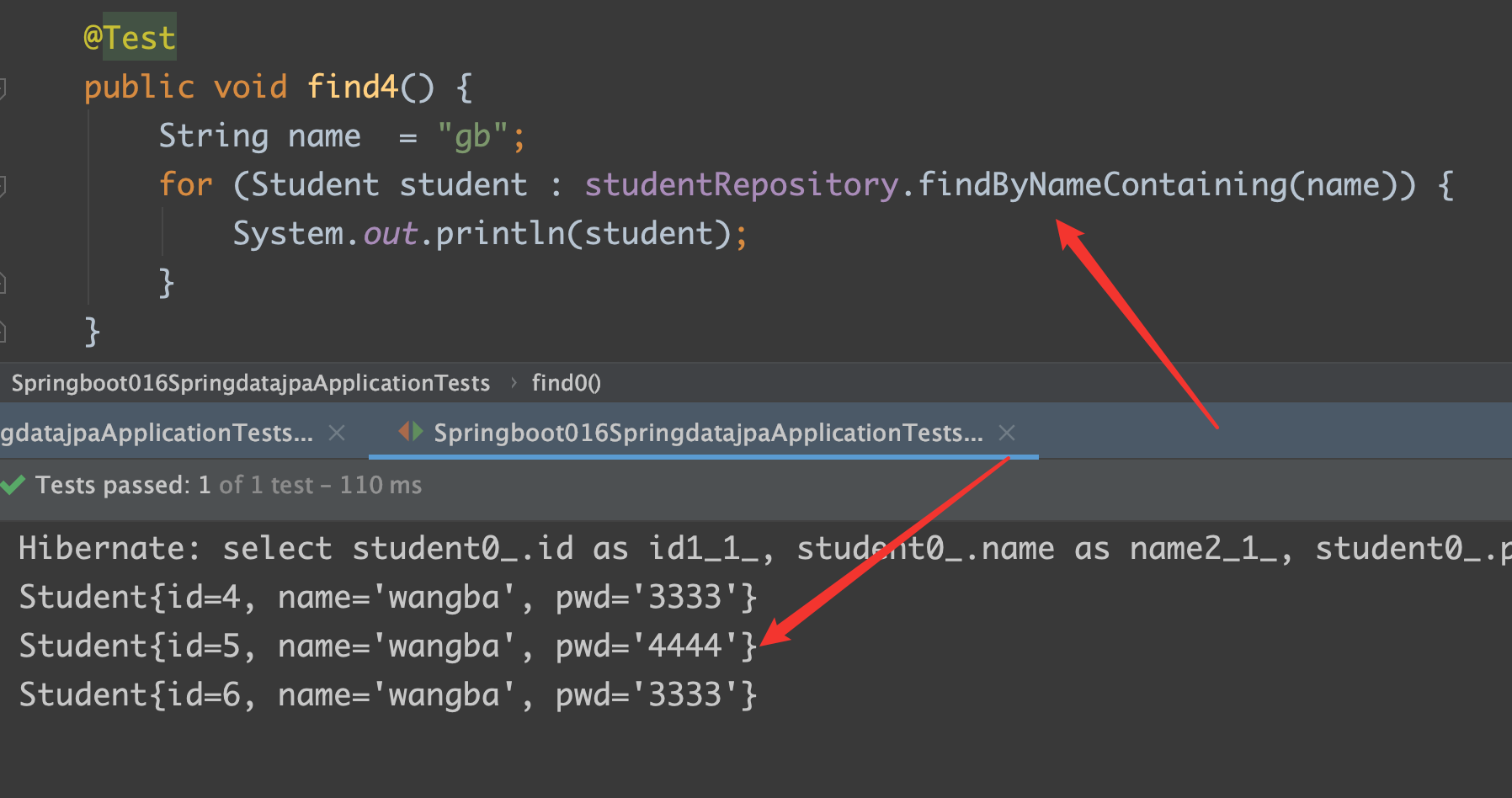
findByNameContainingOrderByIdDesc
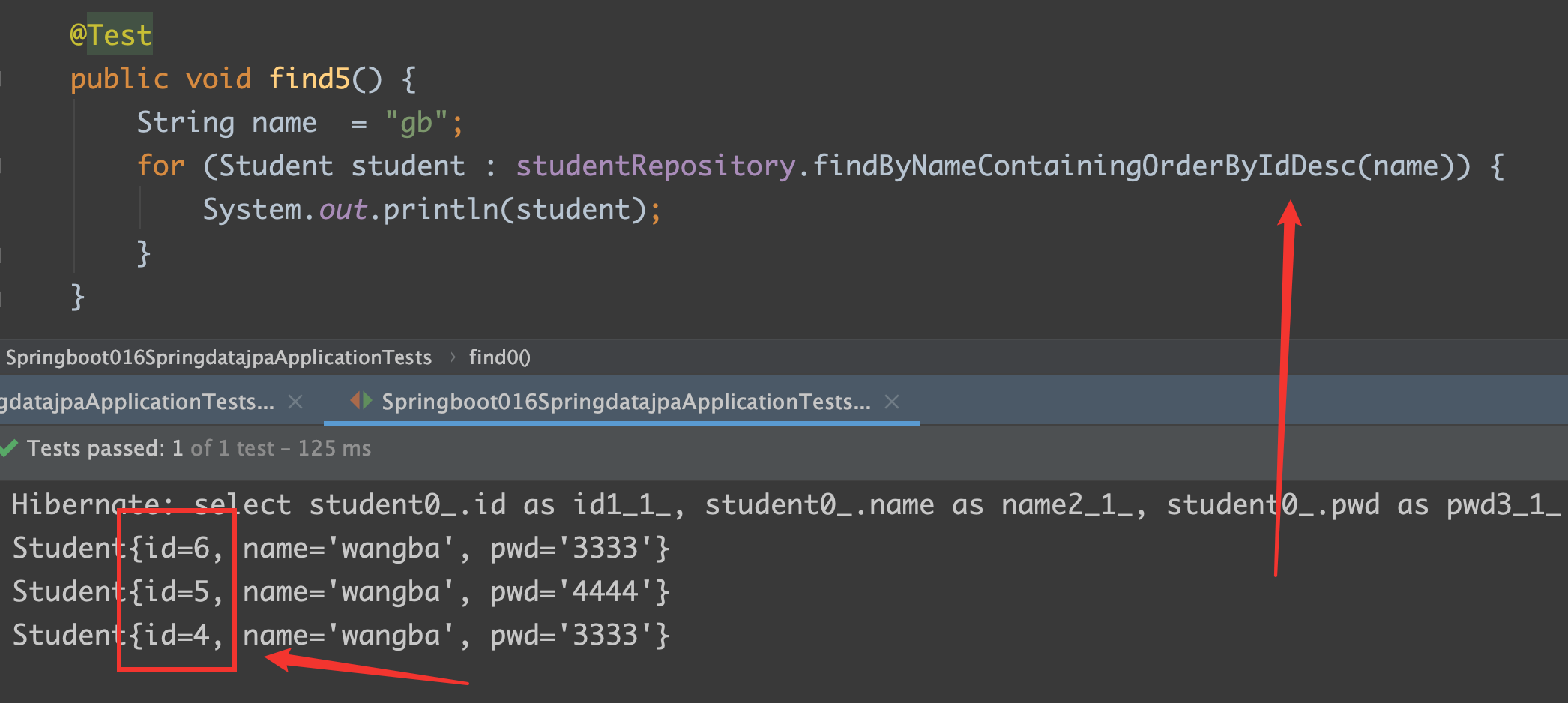
四、分页查询
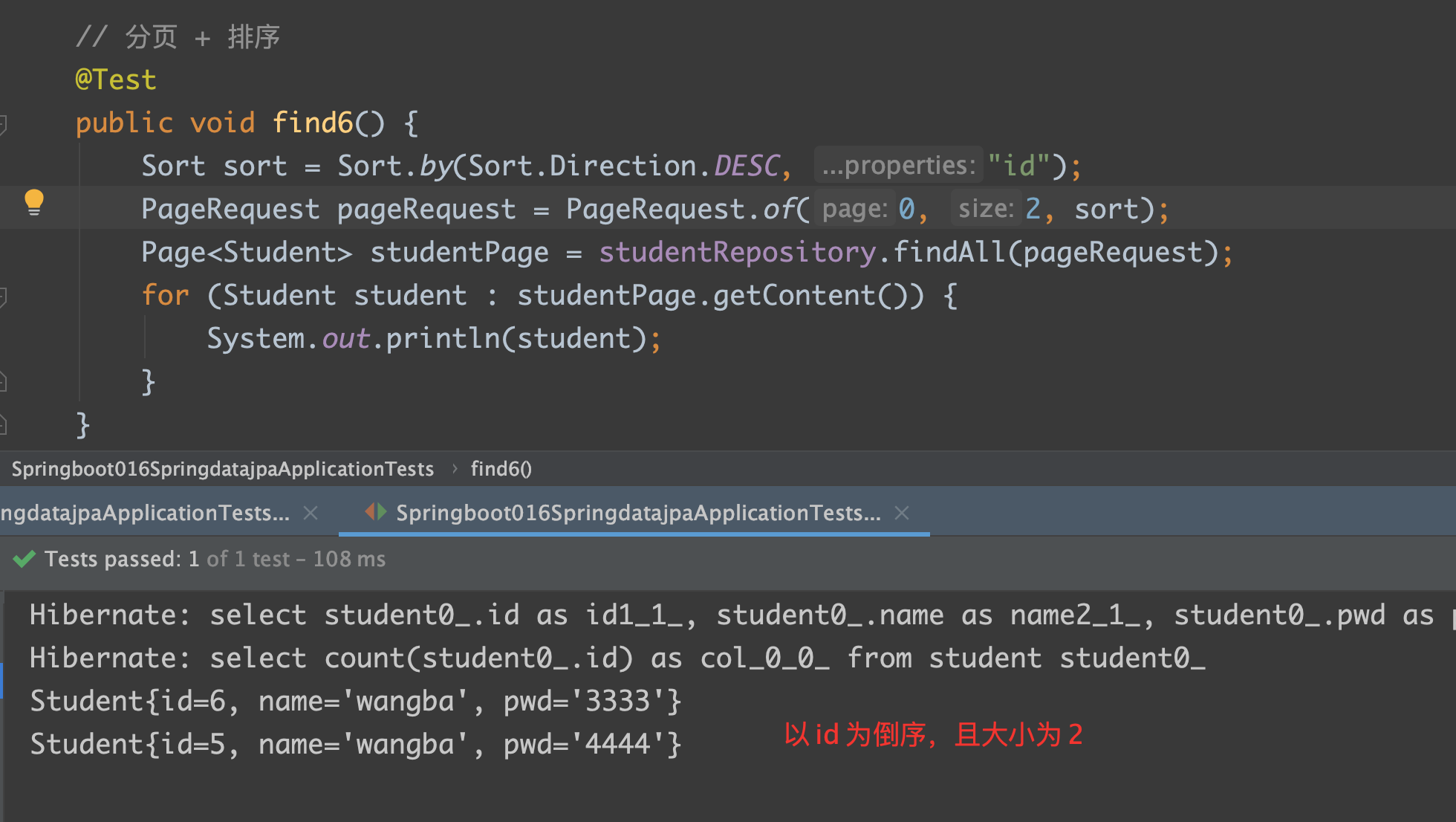
1 | // 分页 + 排序 |
注:
- Sort.by(排序方式, 排序字段)
- PageRequest.of(第多少页,页大小) ——–> 一般是写一个 PageUtils
Test
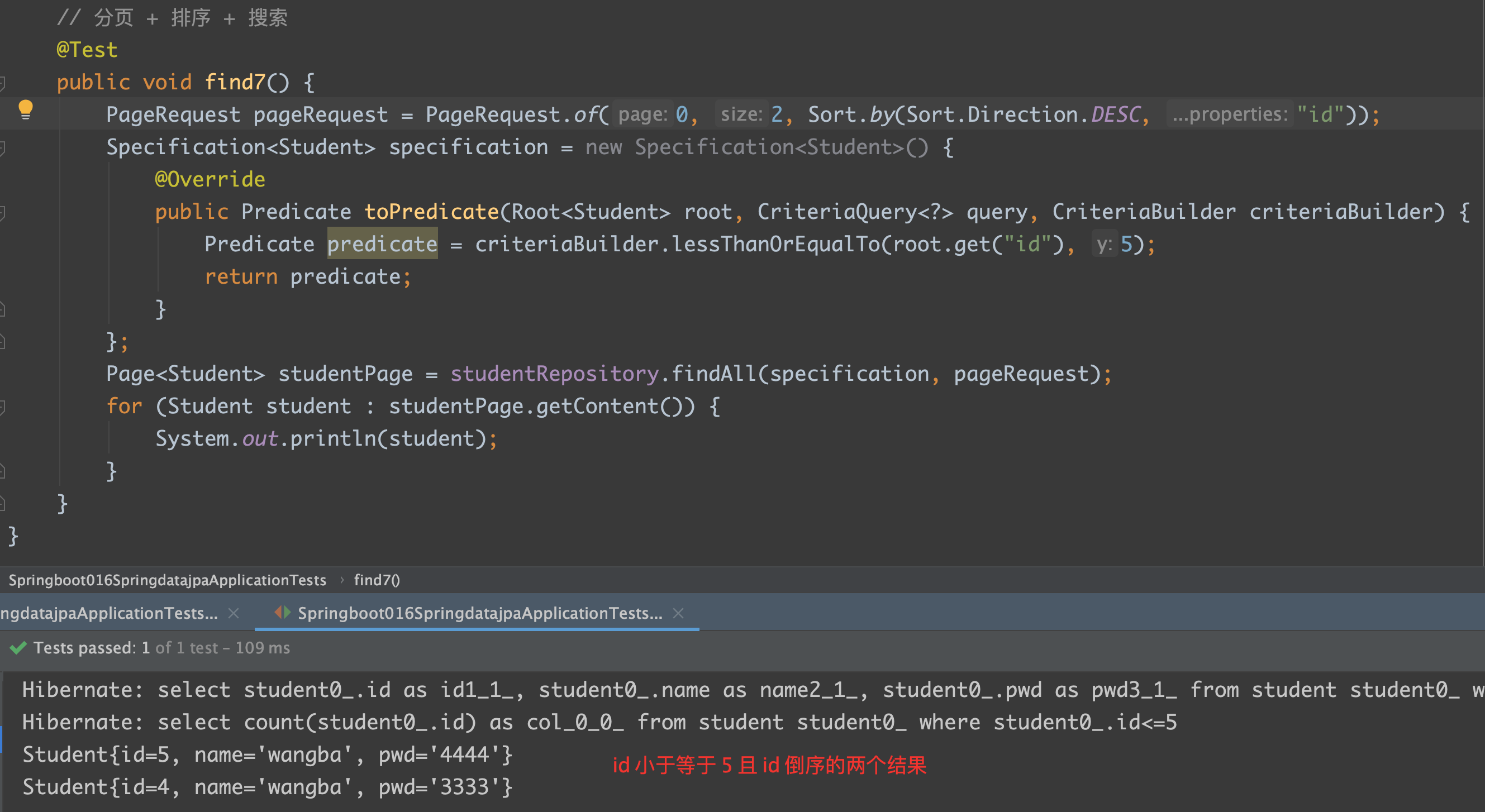
五、动态查询
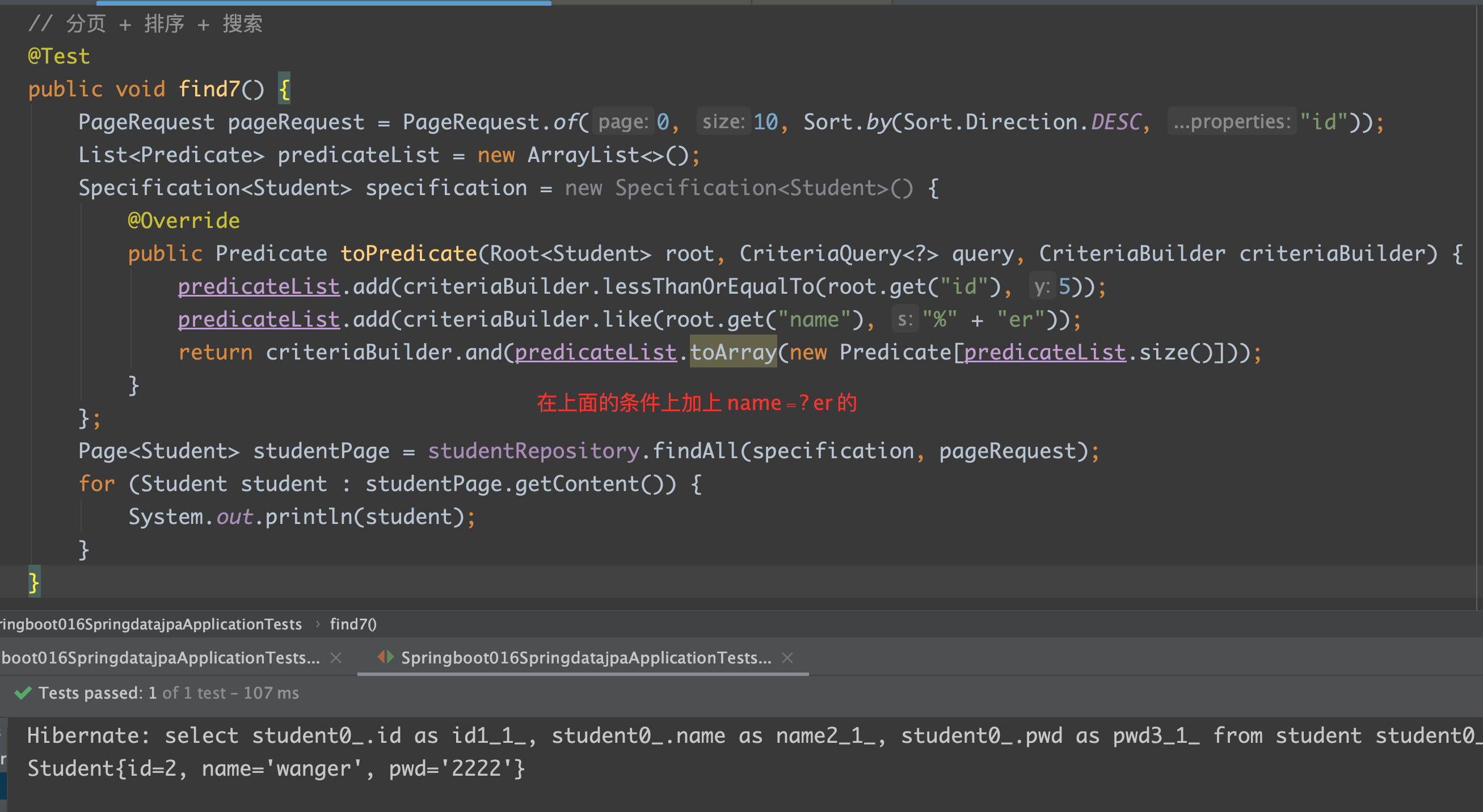
1 | // 分页 + 排序 + 搜索 |
注:
root: 代表查询的实体类
query: 可以从中得到 Root 对象
criteriaBuilder: 用于创建 Criteria 相关对象的工厂
Predicate: 代表一个查询条件
Test:
多条件:
1 | // 分页 + 排序 + 搜索 |
Test: