SpringBoot整合Spring Data JPA 之多条件搜索工具类
一、OverView 在前面已经介绍过了 SpringBoot 整合 JPA 了,但是一般在公司业务中,如果出现很多次多条件搜索查询的情况,那么就会用大量冗余代码了;再结合注解的思想。本次将公共部分提取出来,并用注解的方式进行操作,可以参考前面使用注解进行 AOP 处理日志 ,也符合了 SpringBoot 的思想。
二、BaseQuery QueryWord
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 @Target(ElementType.FIELD) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) public @interface QueryWord { String column () default "" ; MatchType func () default MatchType.equal ; boolean nullable () default false boolean empty () default false BetweenType type () default BetweenType.datetime ; }
注:注解类,只要在要查询的属性上加上相应的注解即可
MatchType
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 public enum MatchType { equal, gt, ge, lt, le, notEqual, like, notLike, between, greaterThan, greaterThanOrEqualTo, lessThan, lessThanOrEqualTo }
注:枚举类,可以对比注释进行理解
BetweenType
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public enum BetweenType { datetime, number_long, number_integer }
注:对应上面 QueryWord中的 BetweenType ,可以对时间或数字之间的属性进行注解
BaseQuery
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 public abstract class BaseQuery <T > private int pageNum = 0 ; private int pageSize = 10 ; private static Map<Class, List<Field>> fieldCache = new HashMap<>(); public abstract Specification<T> toSpec () public Pageable toPageable () return PageRequest.of(pageNum, pageSize); } public Pageable toPageable (Sort sort) return PageRequest.of(pageNum, pageSize, sort); } protected Specification<T> toSpecWithAnd () return this .toSpecWithLogicType("and" ); } protected Specification<T> toSpecWithOr () return this .toSpecWithLogicType("or" ); } @SuppressWarnings({ "rawtypes", "unchecked" }) private Specification<T> toSpecWithLogicType (final String logicType) final BaseQuery outerThis = this ; Specification<T> specification = new Specification<T>() { @Override public Predicate toPredicate (Root<T> root, CriteriaQuery<?> query, CriteriaBuilder cb) Class clazz = outerThis.getClass(); List<Field> fields = fieldCache.get(clazz); if (fields == null ) { fields = getAllFieldsWithRoot(clazz); fieldCache.put(clazz, fields); } List<Predicate> predicates = new ArrayList<>(fields.size()); for (Field field : fields) { QueryWord qw = field.getAnnotation(QueryWord.class); if (qw == null ) { continue ; } String column = qw.column(); if (column.equals("" )) { column = field.getName(); } field.setAccessible(true ); try { Object value = field.get(outerThis); if (value == null && !qw.nullable()) { continue ; } if (value != null && String.class.isAssignableFrom(value.getClass())) { String s = (String) value; if (s.equals("" ) && !qw.empty()) { continue ; } } Path path = root.get(column); switch (qw.func()) { case equal: predicates.add(cb.equal(path, value)); break ; case like: predicates.add(cb.like(path, "%" + value + "%" )); break ; case gt: predicates.add(cb.gt(path, (Number) value)); break ; case lt: predicates.add(cb.lt(path, (Number) value)); break ; case ge: predicates.add(cb.ge(path, (Number) value)); break ; case le: predicates.add(cb.le(path, (Number) value)); break ; case notEqual: predicates.add(cb.notEqual(path, value)); break ; case notLike: predicates.add(cb.notLike(path, "%" + value + "%" )); break ; case greaterThan: predicates.add(cb.greaterThan(path, (Comparable) value)); break ; case greaterThanOrEqualTo: predicates.add(cb.greaterThanOrEqualTo(path, (Comparable) value)); break ; case lessThan: predicates.add(cb.lessThan(path, (Comparable) value)); break ; case lessThanOrEqualTo: predicates.add(cb.lessThanOrEqualTo(path, (Comparable) value)); break ; case between: switch (qw.type()) { case datetime: List<Date> dateList = (List<Date>) value; predicates.add(cb.between(path, dateList.get(0 ), dateList.get(1 ))); break ; case number_long: List<Long> longList = (List<Long>) value; predicates.add(cb.between(path, longList.get(0 ), longList.get(1 ))); break ; case number_integer: List<Integer> integerList = (List<Integer>) value; predicates.add(cb.between(path, integerList.get(0 ), integerList.get(1 ))); break ; } } } catch (Exception e) { continue ; } } Predicate p = null ; if (logicType == null || logicType.equals("" ) || logicType.equals("and" )) { p = cb.and(predicates.toArray(new Predicate[predicates.size()])); } else if (logicType.equals("or" )) { p = cb.or(predicates.toArray(new Predicate[predicates.size()])); } return p; } }; return specification; } private List<Field> getAllFieldsWithRoot (Class<?> clazz) List<Field> fieldList = new ArrayList<>(); Field[] dFields = clazz.getDeclaredFields(); if (null != dFields && dFields.length > 0 ) { fieldList.addAll(Arrays.asList(dFields)); } Class<?> superClass = clazz.getSuperclass(); if (superClass == Object.class) { return Arrays.asList(dFields); } List<Field> superFields = getAllFieldsWithRoot(superClass); if (null != superFields && !superFields.isEmpty()) { for (Field field : superFields) { if (!fieldList.contains(field)) { fieldList.add(field); } } } return fieldList; } public int getPageIndex () return pageNum; } public void setPageIndex (int pageIndex) this .pageNum = pageIndex; } public int getPageSize () return pageSize; } public void setPageSize (int pageSize) this .pageSize = pageSize; } }
注:最关键的类
所有后面要查询的类都要继承它
简单的理解:通过反射获取注解上的字段信息,构造相应的搜索条件
三、Test StudentQuery
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 public class StudentQuery extends BaseQuery @QueryWord(column = "id", func = MatchType.equal) private Long id; @QueryWord(func = MatchType.like) private String name; @Override public Specification toSpec () return super .toSpecWithOr(); } }
在这个查询中,使用的是 or 查询,测试类如下:
Test
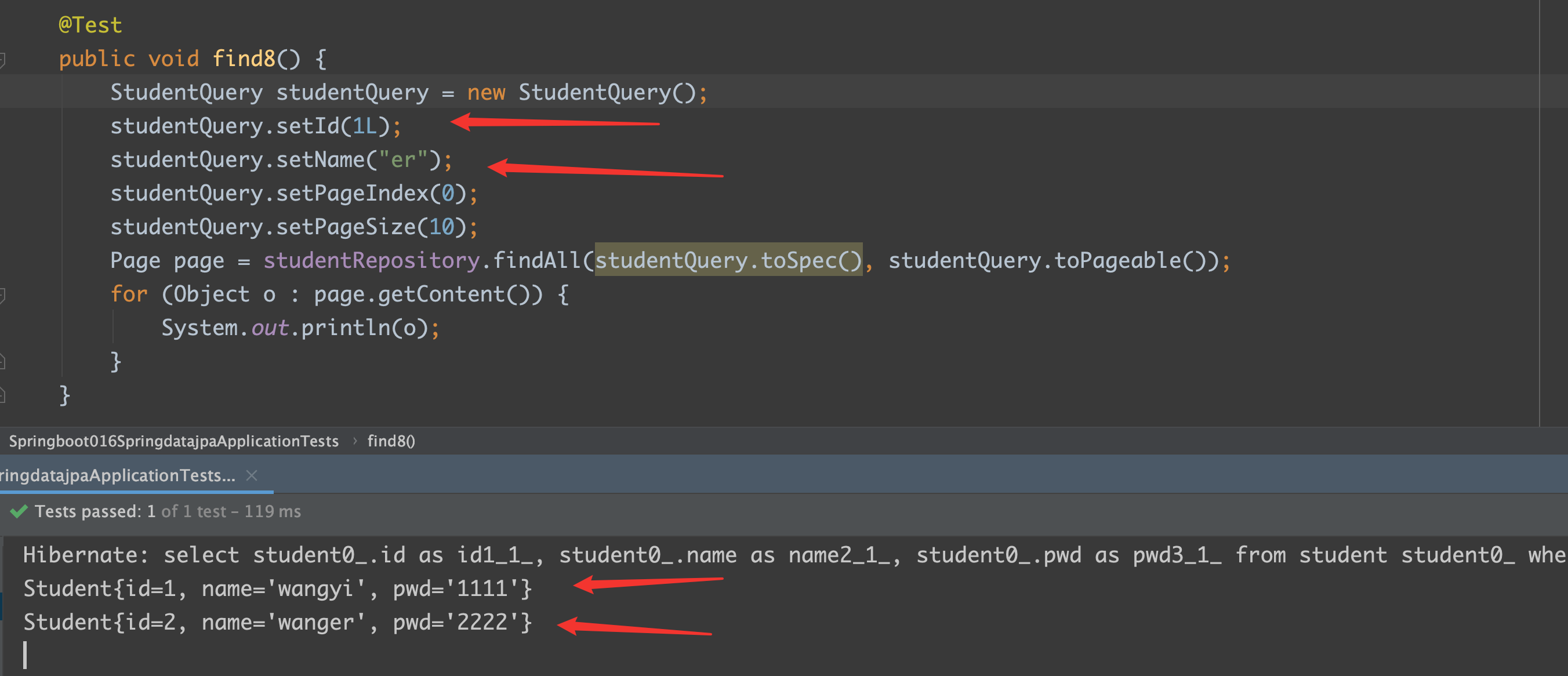
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 @Test public void find8 () StudentQuery studentQuery = new StudentQuery(); studentQuery.setId(1L ); studentQuery.setName("er" ); studentQuery.setPageIndex(0 ); studentQuery.setPageSize(10 ); Page page = studentRepository.findAll(studentQuery.toSpec(), studentQuery.toPageable()); for (Object o : page.getContent()) { System.out.println(o); } }
注:构造的条件是 id = 1的,或者 name = ? er ? 的 student
结果
通过这个例子简单捋一下整个过程:
通过 studentQuery.toSpec() 调用父类 BaseQuery;
在 BaseQuery 中,通过反射获得打了相应注解上的字段信息;
将字段信息加到搜索条件中,进行 or 或者 and 连接
注:如果你的业务中只用了很少的条件或者只用极个别的多条件查询,可以不用这个工具类