21. Merge Two Sorted Lists Easy
Merge two sorted linked lists and return it as a new sorted list. The new list should be made by splicing together the nodes of the first two lists.
Example 1:

1 | Input: l1 = [1,2,4], l2 = [1,3,4] |
Example 2:
1 | Input: l1 = [], l2 = [] |
Example 3:
1 | Input: l1 = [], l2 = [0] |
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in both lists is in the range
[0, 50]. -100 <= Node.val <= 100- Both
l1andl2are sorted in non-decreasing order.
思路:
思路一:迭代法
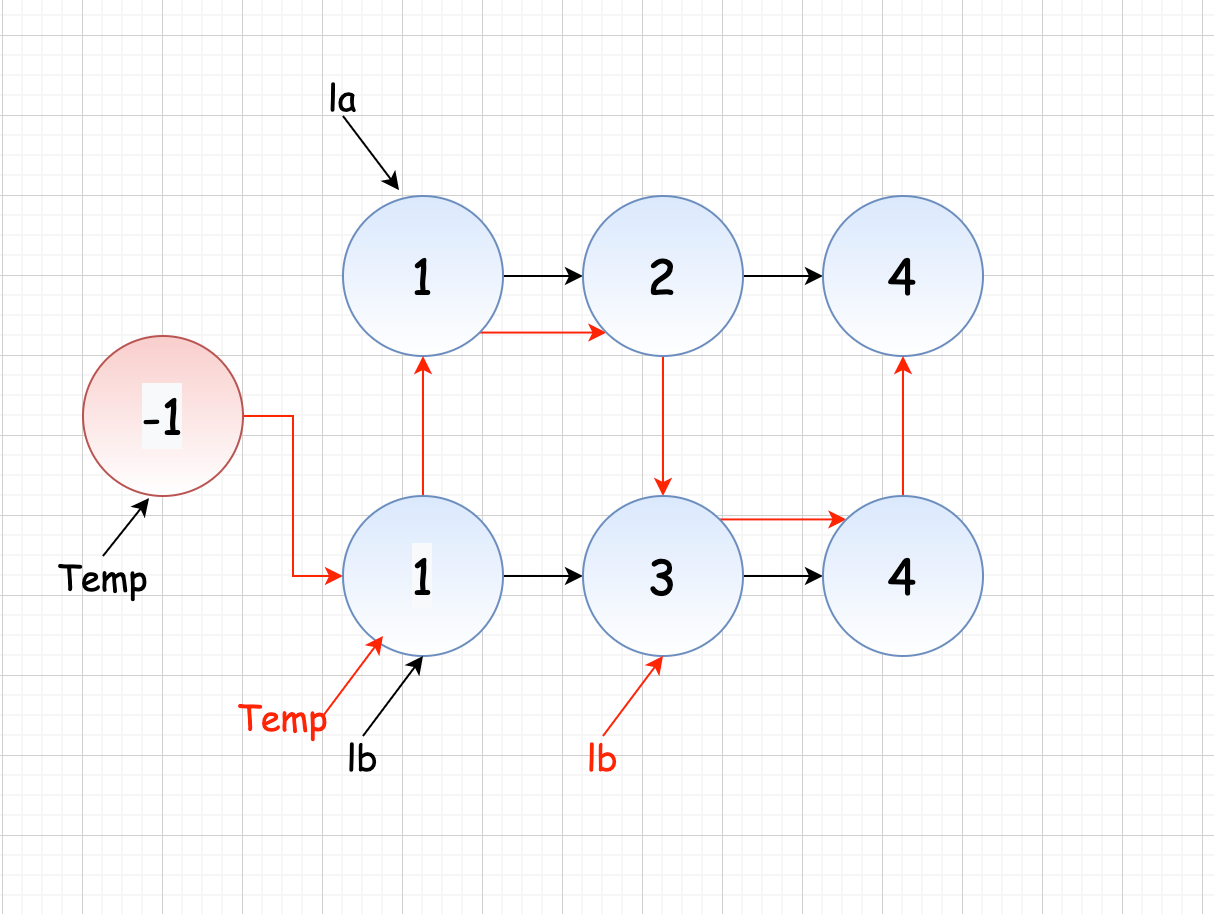
设置一个头结点,随后开始比较两个链表的结点值大小,具体逻辑可以将下面的图和代码逻辑联系起来:
代码:
1 | public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) { |
时间复杂度:O(m + n)
空间复杂度:O(1)
思路二:递归法
递归最重要的两个点:
- 递归的出口,在本题里面就是当其中的一个链表为空,直接返回另外一个链表即可
- 要进行递归,传入参数后的结果应该是已经确定的了,在这里就是链表已经排好序了
举个例子:如果现在是
1 | 链表la:1 -> 3 -> 5 |
进行第一次递归时:要比较 1 和 2 的大小,发现 1 < 2,此时只需要将 1.next = mergeTwoLists(3, 2) 就行了,不要去想 mergeTwoLists(3, 2) 怎么来的,要把它当作已经确定的值就行,而 mergeTwoLists(3, 2) 的值可以看作是下面这两个链表的进行 mergeTwoLists 的结果
1 | 链表la:3 -> 5 |
代码:
1 | public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) { |
时间复杂度:O(m + n)
空间复杂度:O(m + n)
- 由于递归是调用栈的,每递归一次需要一个栈帧